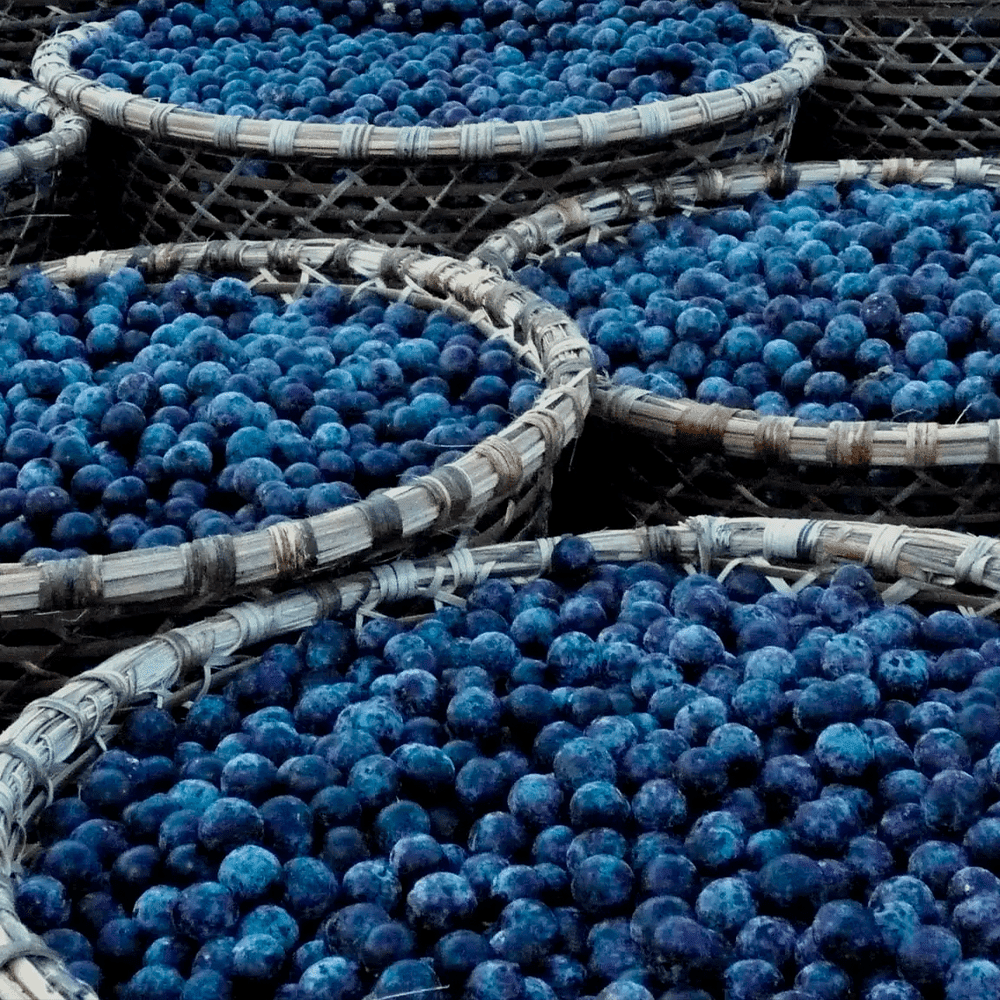
Extractivism is an economic activity that consists of the collection and sustainable use of natural resources present in the Amazon forest, such as plants, fruits, seeds, oils and other plant species. This activity is important for the forest ecosystem because it can be carried out in a way that preserves the biodiversity and ecological balance of the region.
The selective collection of plant products is a form of sustainable management of forest natural resources, as it allows the renewal of natural resources and the conservation of biodiversity. The activity is equally relevant for forest communities, as it is an economic development alternative for local communities, encouraging the conservation of Amazonian biodiversity and reducing pressure on natural resources and can be a way of promoting species conservation threatened with extinction, since numerous plants have medicinal properties or are used as inputs in the manufacture of cosmetic and pharmaceutical products. The selective collection of these inputs encourages the conservation of these species, preventing their extinction.
It is important to highlight that plant extraction needs to be carried out in a sustainable and responsible way, with respect for environmental legislation and the rights of local communities. In this way, it is possible to reconcile economic development with the preservation of the environment and the conservation of the biodiversity of the Amazon forest. Extractivism is a way of keeping the forest standing. The relationship between local communities and natural resources is one of interdependence - as these people depend on natural resources for their subsistence - and, therefore, have a direct interest in preserving the forest and conserving natural resources.
The Forest as an Important Source of Sustainable Income
The Amazon is a region rich in natural resources, including a vast variety of plant species. Plant extraction is an important economic activity in the region, as it contributes to income generation and sustainable development. The activity consists of collecting plant products such as fruits, nuts, essential oils, medicinal plants, fibers, among others, without the need to cut or fell trees. These products are used in the food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries, among others. Extractivism is carried out in a sustainable way, respecting the limits of the environment and ensuring the conservation of biodiversity. This means that clear rules are established for the collection of plant products, such as the maximum quantity allowed per individual and the time of year in which collection can be carried out.
It is important that extractivists receive technical and financial support to improve their collection and processing techniques, guaranteeing the quality of the products and their competitiveness in the market. It is also essential that there is strict control over the marketing of products, avoiding the exploitation and misuse of natural resources.
Extractive Diversity in the Triple Frontier
Each country that covers the Amazon Forest has its own specificities in relation to plant extraction. Due to the geographic extension of the Forest, each location has its own legal, cultural and extracted product specificities.
In Brazil: the collection of plant products is regulated by the Forest Products Origin Control System (SISFLORA), which was created with the aim of controlling the production, transport, storage and commercialization of forest products in the country.
The most extracted products from the Amazon Forest are Brazil nuts, rubber, açaí, andiroba, cupuaçu, peach palm, copaíba, babassu oil and cocoa. These products are used in various industries, such as food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, among others.
- Brazil nuts are highly valued for their nutritional properties and for being rich in selenium. It is used in the manufacture of cereal bars, chocolates, granolas, among others. Companies such as Amaggi and Cargill are among the largest buyers of Brazil nuts in the Amazon region.
- Natural rubber is an important product for the automobile industry, being used in the manufacture of tires, belts and other parts. Companies such as Pirelli and Michelin are among the largest buyers of natural rubber in the region.
- Açaí is a product widely used in the food industry, in drinks, ice cream, jellies and other products. Companies such as Ambev and Nestlé are major buyers of açaí in the region.
- Andiroba is used in the manufacture of cosmetic and medicinal products, due to its medicinal and anti-inflammatory properties. Companies such as Natura and the multinational L'Oreal use andiroba in their products.
- The peach palm is a palm tree that produces edible fruits, widely used in regional cuisine. Companies such as Vigor and Frooty use peach palm in their food products.
- Copaiba is used in the manufacture of medicines and cosmetics, due to its anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Companies such as Johnson & Johnson and Natura use copaíba in their products.
- Babassu oil is used in the manufacture of cosmetic products, such as shampoos and soaps. Companies like Granado and L'Oreal use babassu oil in their products.
- Cocoa is an important product for the food industry, being used in the manufacture of chocolates and other products. Companies such as Nestlé and Mondelez International use cocoa in the region.
In Peru: The collection of forest products in Peru is of great importance for the country's economy and local communities. This activity is regulated by the Forestry and Wildlife Law, which establishes rules for granting authorizations for the exploitation of forest products, as well as for controlling the production and commercialization of these products.
Among the most collected products in Peru are Brazil nuts, cocoa, rosewood, copaíba and cumaru. These products are used in various industries, such as food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, among others.
- Brazil nuts are a product highly valued for their nutritional properties and are widely used in the food industry, in products such as cereal bars, chocolates, granola, among others. Companies such as Barry Callebaut and Nestlé are among the largest buyers of Brazil nuts in the country.
- Cocoa is an important product for the food industry, being used in the manufacture of chocolates and other products. Companies such as Nestlé and Mondelez International use Peruvian cocoa to make chocolates.
- Rosewood essential oil is used in the production of cosmetics and perfumes due to its pleasant aroma and therapeutic properties. Companies like Natura and L'Occitane use this oil in their beauty products.
- Copaiba is used in the manufacture of medicines and cosmetics, due to its anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Companies like Natura and L'Oreal use copaíba in their products.
- Cumaru is used in the food industry, in products such as ice cream, cakes and cookies, due to its characteristic aroma. Companies such as Frooty and BRF use cumaru in their food products.
In Colombia: The collection of plant products is regulated by the National Environmental System (SINA), which establishes standards and procedures for the exploration, transport, storage and commercialization of forest products. This regulation aims to protect the environment and guarantee the sustainability of extractive activities in the region. Among the most extracted products in Colombia are wood, latex, resin, fruits and medicinal plants. Wood is used in the production of furniture, construction and paper, while latex and resin are used in the manufacture of rubber and adhesives.
Furthermore, medicinal fruits and plants are used for both human consumption and medicinal purposes. There are several companies that use Colombian extractivism products, mainly in the areas of cosmetics, food and medicine. Some of the main companies are:
- Natura: the Brazilian company uses natural ingredients in its products, including medicinal plants from the Colombian Amazon.
- L'Oréal: the French company uses natural ingredients in its product line, including essential oils and plant extracts from Colombia.
- Unilever: the British company uses essential oils and plant extracts from the Colombian Amazon in its line of hair and skin products.
- Herbalife: the American company uses medicinal plants from Colombia in its food supplements and nutritional products.
- Amway: the American company uses fruits and medicinal plants from the Colombian Amazon in its line of nutritional products and dietary supplements.
These companies have adopted sustainable practices in their supply chains, ensuring the preservation of biodiversity and the well-being of local communities that depend on plant extraction in Colombia. Through SINA regulation, the Colombian government guarantees that extractive activities are carried out in a sustainable manner, avoiding predatory exploitation and uncontrolled deforestation. In this way, it is possible to preserve the forest's biodiversity and guarantee food security for local communities, which depend on the region's natural resources.
Extractivism Promotes Food Security in Local Communities
Food security for communities living in the Amazon Rainforest is an important issue that must be considered when discussing plant extractivism. Communities living in the forest depend on natural resources for their subsistence, including collecting fruits, nuts and other plant species.
However, the growing demand for agricultural products and the expansion of the agricultural frontier in the Amazon could pose a threat to the food security of local communities. Environmental degradation, soil contamination and loss of biodiversity can compromise the availability and quality of natural resources used by communities for food.
To ensure food security for forest communities, it is important to promote sustainable agricultural practices that are respectful of the environment, which allow the maintenance of biodiversity and the preservation of natural resources. Furthermore, it is essential to guarantee communities' access to the forest's natural resources, through land regularization, the demarcation of indigenous lands and the promotion of programs aimed at sustainable development.
Preserve Brasil is one of the main organizations that develops projects to support plant extractivism, a sustainable economic activity for communities in the Brazilian Amazon region. These projects aim to develop conditions for these people to have food security, through the adoption of sustainable practices for exploiting natural resources and equitable access to these resources. Through social organization, the application of serious programs committed to human development, and the association of plant extractivism with the Agroforestry System, forest communities guarantee access to healthy and quality food, preserving biodiversity and the environment.
Discover the Program Green Crafts: